本文章由 WyOJ Shojo 从洛谷专栏拉取,原发布时间为 2024-02-28 13:56:38
F:
Yet Another Broken Keyboard
题面翻译
题目描述
$Norge$,找到了一个长度为$n$的字符串$s$($s$仅由小写英文字母构成),他想把这个字符串的所有$\frac{n(n+1)}{2}$个连续非空子串都打出来
可是,他发现他的键盘坏了,只能打出26字母中的$k$个
这$k$个字母分别为:$c_1,c_2,c_3,\dots ,c_k$
请求出用这个坏掉的键盘,最多能打出多少个字符串$s$的连续非空子串
输入格式
第一行两个整数 $n,k$ ,表示字符串$s$的长度,和能用字母的数量
第二行一个长度为$n$字符串$s$
第三行,$k$个由空格隔开的字母,表示键盘上没有坏掉的字母
输出格式
一行一个整数,表示用这个坏掉的键盘,最多能打出多少个字符串$s$的连续非空子串
数据范围
$1\leq n \le 2\cdot 10^5$,$1\leq k \le 26$
感谢 @_Wolverine 提供的翻译
题目描述
Recently, Norge found a string $ s = s_1 s_2 \ldots s_n $ consisting of $ n $ lowercase Latin letters. As an exercise to improve his typing speed, he decided to type all substrings of the string $ s $ . Yes, all $ \frac{n (n + 1)}{2} $ of them!
A substring of $ s $ is a non-empty string $ x = s[a \ldots b] = s_{a} s_{a + 1} \ldots s_{b} $ ( $ 1 \leq a \leq b \leq n $ ). For example, "auto" and "ton" are substrings of "automaton".
Shortly after the start of the exercise, Norge realized that his keyboard was broken, namely, he could use only $ k $ Latin letters $ c_1, c_2, \ldots, c_k $ out of $ 26 $ .
After that, Norge became interested in how many substrings of the string $ s $ he could still type using his broken keyboard. Help him to find this number.
输入格式
The first line contains two space-separated integers $ n $ and $ k $ ( $ 1 \leq n \leq 2 \cdot 10^5 $ , $ 1 \leq k \leq 26 $ ) — the length of the string $ s $ and the number of Latin letters still available on the keyboard.
The second line contains the string $ s $ consisting of exactly $ n $ lowercase Latin letters.
The third line contains $ k $ space-separated distinct lowercase Latin letters $ c_1, c_2, \ldots, c_k $ — the letters still available on the keyboard.
输出格式
Print a single number — the number of substrings of $ s $ that can be typed using only available letters $ c_1, c_2, \ldots, c_k $ .
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
7 2
abacaba
a b
样例输出 #1
12
样例 #2
样例输入 #2
10 3
sadfaasdda
f a d
样例输出 #2
21
样例 #3
样例输入 #3
7 1
aaaaaaa
b
样例输出 #3
0
提示
In the first example Norge can print substrings $ s[1\ldots2] $ , $ s[2\ldots3] $ , $ s[1\ldots3] $ , $ s[1\ldots1] $ , $ s[2\ldots2] $ , $ s[3\ldots3] $ , $ s[5\ldots6] $ , $ s[6\ldots7] $ , $ s[5\ldots7] $ , $ s[5\ldots5] $ , $ s[6\ldots6] $ , $ s[7\ldots7] $ .
G:
Ternary XOR
题面翻译
Ternary 数是只含有0、1、2的数。例如 $1022,11,21,2002$ 。
你会得到一个 ternary 数 $x$ 。它的左起第一位一定是 $2$ 。而其它位可以是 $0,1,2$ 。
让我们定义两个 $n$ 位的 ternary 数 $a$ 和 $b$ 之间的异或运算符号 $\bigodot$ 。 $a\bigodot b=c$ 。 $c$ 也是一个 $n$ 位的 ternary 数。 $c_i=(a_i+b_i)\%3$ 。例如, $10222\bigodot 11021=21210$ 。
给出几组 $c$ 与 $n$ ,求最小的 $max(a,b)$。 有多组数据。
题目描述
A number is ternary if it contains only digits $ 0 $ , $ 1 $ and $ 2 $ . For example, the following numbers are ternary: $ 1022 $ , $ 11 $ , $ 21 $ , $ 2002 $ .
You are given a long ternary number $ x $ . The first (leftmost) digit of $ x $ is guaranteed to be $ 2 $ , the other digits of $ x $ can be $ 0 $ , $ 1 $ or $ 2 $ .
Let's define the ternary XOR operation $ \odot $ of two ternary numbers $ a $ and $ b $ (both of length $ n $ ) as a number $ c = a \odot b $ of length $ n $ , where $ c_i = (a_i + b_i) \% 3 $ (where $ \% $ is modulo operation). In other words, add the corresponding digits and take the remainders of the sums when divided by $ 3 $ . For example, $ 10222 \odot 11021 = 21210 $ .
Your task is to find such ternary numbers $ a $ and $ b $ both of length $ n $ and both without leading zeros that $ a \odot b = x $ and $ max(a, b) $ is the minimum possible.
You have to answer $ t $ independent test cases.
输入格式
The first line of the input contains one integer $ t $ ( $ 1 \le t \le 10^4 $ ) — the number of test cases. Then $ t $ test cases follow. The first line of the test case contains one integer $ n $ ( $ 1 \le n \le 5 \cdot 10^4 $ ) — the length of $ x $ . The second line of the test case contains ternary number $ x $ consisting of $ n $ digits $ 0, 1 $ or $ 2 $ . It is guaranteed that the first digit of $ x $ is $ 2 $ . It is guaranteed that the sum of $ n $ over all test cases does not exceed $ 5 \cdot 10^4 $ ( $ \sum n \le 5 \cdot 10^4 $ ).
输出格式
For each test case, print the answer — two ternary integers $ a $ and $ b $ both of length $ n $ and both without leading zeros such that $ a \odot b = x $ and $ max(a, b) $ is the minimum possible. If there are several answers, you can print any.
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
4
5
22222
5
21211
1
2
9
220222021
样例输出 #1
11111
11111
11000
10211
1
1
110111011
110111010
H:
Array and Operations
题面翻译
给定 $n$ 个数和一个数 $k$,要求对这 $n$ 个数进行 $k$ 次操作,每次操作取出两个数 $a_i,a_j (i\neq j)$,并将 $\lfloor \frac{a_i}{a_j} \rfloor$ 加进得分中,其中 $\lfloor \frac{x}{y} \rfloor$ 为不超过 $\frac{x}{y}$ 的最大整数。
$k$ 次操作后,将剩下的 $n-2k$ 个数直接加入到得分中。
求最终得分的最小值。
题目描述
You are given an array $ a $ of $ n $ integers, and another integer $ k $ such that $ 2k \le n $ .
You have to perform exactly $ k $ operations with this array. In one operation, you have to choose two elements of the array (let them be $ a_i $ and $ a_j $ ; they can be equal or different, but their positions in the array must not be the same), remove them from the array, and add $ \lfloor \frac{a_i}{a_j} \rfloor $ to your score, where $ \lfloor \frac{x}{y} \rfloor $ is the maximum integer not exceeding $ \frac{x}{y} $ .
Initially, your score is $ 0 $ . After you perform exactly $ k $ operations, you add all the remaining elements of the array to the score.
Calculate the minimum possible score you can get.
输入格式
The first line of the input contains one integer $ t $ ( $ 1 \le t \le 500 $ ) — the number of test cases.
Each test case consists of two lines. The first line contains two integers $ n $ and $ k $ ( $ 1 \le n \le 100 $ ; $ 0 \le k \le \lfloor \frac{n}{2} \rfloor $ ).
The second line contains $ n $ integers $ a_1, a_2, \dots, a_n $ ( $ 1 \le a_i \le 2 \cdot 10^5 $ ).
输出格式
Print one integer — the minimum possible score you can get.
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
5
7 3
1 1 1 2 1 3 1
5 1
5 5 5 5 5
4 2
1 3 3 7
2 0
4 2
9 2
1 10 10 1 10 2 7 10 3
样例输出 #1
2
16
0
6
16
提示
Let's consider the example test.
In the first test case, one way to obtain a score of $ 2 $ is the following one:
- choose $ a_7 = 1 $ and $ a_4 = 2 $ for the operation; the score becomes $ 0 + \lfloor \frac{1}{2} \rfloor = 0 $ , the array becomes $ [1, 1, 1, 1, 3] $ ;
- choose $ a_1 = 1 $ and $ a_5 = 3 $ for the operation; the score becomes $ 0 + \lfloor \frac{1}{3} \rfloor = 0 $ , the array becomes $ [1, 1, 1] $ ;
- choose $ a_1 = 1 $ and $ a_2 = 1 $ for the operation; the score becomes $ 0 + \lfloor \frac{1}{1} \rfloor = 1 $ , the array becomes $ [1] $ ;
- add the remaining element $ 1 $ to the score, so the resulting score is $ 2 $ .
In the second test case, no matter which operations you choose, the resulting score is $ 16 $ .
In the third test case, one way to obtain a score of $ 0 $ is the following one:
- choose $ a_1 = 1 $ and $ a_2 = 3 $ for the operation; the score becomes $ 0 + \lfloor \frac{1}{3} \rfloor = 0 $ , the array becomes $ [3, 7] $ ;
- choose $ a_1 = 3 $ and $ a_2 = 7 $ for the operation; the score becomes $ 0 + \lfloor \frac{3}{7} \rfloor = 0 $ , the array becomes empty;
- the array is empty, so the score doesn't change anymore.
In the fourth test case, no operations can be performed, so the score is the sum of the elements of the array: $ 4 + 2 = 6 $ .
I:
Bricks and Bags
题面翻译
hhoppitree 有 $n$ 根木棍,其中第 $i$ 根木棍的长度为 $a_i$,他想要将它们放置在三个背包中,使得每个背包中至少有一根木棍。
他的好朋友会从每个背包中选出一根木棍,假设从三个背包中取出的木棍的长度分别为 $x,y,z$,则他会送给 hhoppitree 一共 $|x-y|+|y-z|$ 瓶可乐,显然,他的朋友会最小化这个数的值。
hhoppitree 想通过适当的分配,使得这个数的最小可能值最大,他想知道这个最大值是多少。
题目描述
There are $ n $ bricks numbered from $ 1 $ to $ n $ . Brick $ i $ has a weight of $ a_i $ .
Pak Chanek has $ 3 $ bags numbered from $ 1 $ to $ 3 $ that are initially empty. For each brick, Pak Chanek must put it into one of the bags. After this, each bag must contain at least one brick.
After Pak Chanek distributes the bricks, Bu Dengklek will take exactly one brick from each bag. Let $ w_j $ be the weight of the brick Bu Dengklek takes from bag $ j $ . The score is calculated as $ |w_1 - w_2| + |w_2 - w_3| $ , where $ |x| $ denotes the absolute value of $ x $ .
It is known that Bu Dengklek will take the bricks in such a way that minimises the score. What is the maximum possible final score if Pak Chanek distributes the bricks optimally?
输入格式
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains an integer $ t $ ( $ 1 \leq t \leq 2 \cdot 10^4 $ ) — the number of test cases. The following lines contain the description of each test case.
The first line of each test case contains an integer $ n $ ( $ 3 \leq n \leq 2 \cdot 10^5 $ ) — the number of bricks.
The second line of each test case contains $ n $ integers $ a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n $ ( $ 1 \leq a_i \leq 10^9 $ ) — the weights of the bricks.
It is guaranteed that the sum of $ n $ over all test cases does not exceed $ 2 \cdot 10^5 $ .
输出格式
For each test case, output a line containing an integer representing the maximum possible final score if Pak Chanek distributes the bricks optimally.
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
3
5
3 1 5 2 3
4
17 8 19 45
8
265 265 265 265 265 265 265 265
样例输出 #1
6
63
0
提示
In the first test case, one way of achieving a final score of $ 6 $ is to do the following:
- Put bricks $ 1 $ , $ 4 $ , and $ 5 $ into bag $ 1 $ .
- Put brick $ 3 $ into bag $ 2 $ .
- Put brick $ 2 $ into bag $ 3 $ .
If Pak Chanek distributes the bricks that way, a way Bu Dengklek can take the bricks is:
- Take brick $ 5 $ from bag $ 1 $ .
- Take brick $ 3 $ from bag $ 2 $ .
- Take brick $ 2 $ from bag $ 3 $ .
The score is $ |a_5 - a_3| + |a_3 - a_2| = |3 - 5| + |5 - 1| = 6 $ . It can be shown that Bu Dengklek cannot get a smaller score from this distribution.
It can be shown that there is no other distribution that results in a final score bigger than $ 6 $ .
J:
Binary Search
题面翻译
给定三个正整数 $n,x,pos$,请你求出满足以下条件的数组 $a$ 的个数:
请将答案对 $1e9+7$ 取模后输出。
翻译 by vectorwyx
题目描述
Andrey thinks he is truly a successful developer, but in reality he didn't know about the binary search algorithm until recently. After reading some literature Andrey understood that this algorithm allows to quickly find a certain number $ x $ in an array. For an array $ a $ indexed from zero, and an integer $ x $ the pseudocode of the algorithm is as follows:
 Note that the elements of the array are indexed from zero, and the division is done in integers (rounding down).
Note that the elements of the array are indexed from zero, and the division is done in integers (rounding down).
Andrey read that the algorithm only works if the array is sorted. However, he found this statement untrue, because there certainly exist unsorted arrays for which the algorithm find $ x $ !
Andrey wants to write a letter to the book authors, but before doing that he must consider the permutations of size $ n $ such that the algorithm finds $ x $ in them. A permutation of size $ n $ is an array consisting of $ n $ distinct integers between $ 1 $ and $ n $ in arbitrary order.
Help Andrey and find the number of permutations of size $ n $ which contain $ x $ at position $ pos $ and for which the given implementation of the binary search algorithm finds $ x $ (returns true). As the result may be extremely large, print the remainder of its division by $ 10^9+7 $ .
输入格式
The only line of input contains integers $ n $ , $ x $ and $ pos $ ( $ 1 \le x \le n \le 1000 $ , $ 0 \le pos \le n - 1 $ ) — the required length of the permutation, the number to search, and the required position of that number, respectively.
输出格式
Print a single number — the remainder of the division of the number of valid permutations by $ 10^9+7 $ .
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
4 1 2
样例输出 #1
6
样例 #2
样例输入 #2
123 42 24
样例输出 #2
824071958
提示
All possible permutations in the first test case: $ (2, 3, 1, 4) $ , $ (2, 4, 1, 3) $ , $ (3, 2, 1, 4) $ , $ (3, 4, 1, 2) $ , $ (4, 2, 1, 3) $ , $ (4, 3, 1, 2) $ .

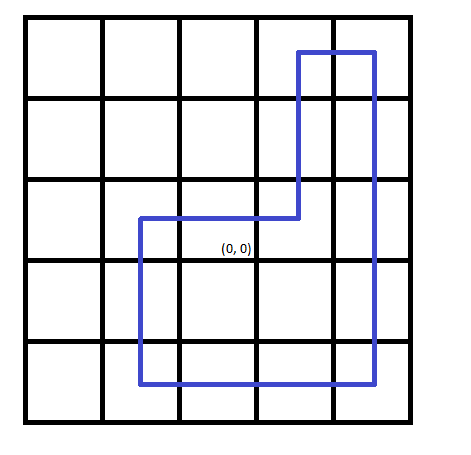 Note that the direction of traverse does not matter Another correct answer to the third test case: "URDDLLLUURDR".
Note that the direction of traverse does not matter Another correct answer to the third test case: "URDDLLLUURDR". Note that the elements of the array are indexed from zero, and the division is done in integers (rounding down).
Note that the elements of the array are indexed from zero, and the division is done in integers (rounding down).

 鲁ICP备2025150228号
鲁ICP备2025150228号