本文章由 WyOJ Shojo 从洛谷专栏拉取,原发布时间为 2025-09-12 16:40:31
考虑到对于已经选择的灯的集合,调整顺序使得能走的距离更远总是不劣的,可以反证法证明。
令 $f_{s}$ 表示已经使用了 $s$ 集合的灯,此时能走的最远距离。
转移的话,就枚举一个新的未使用的灯。
此时,新的灯的照亮的左边界必然就是 $f_s$,现在需要算出这盏灯照亮的右边界。
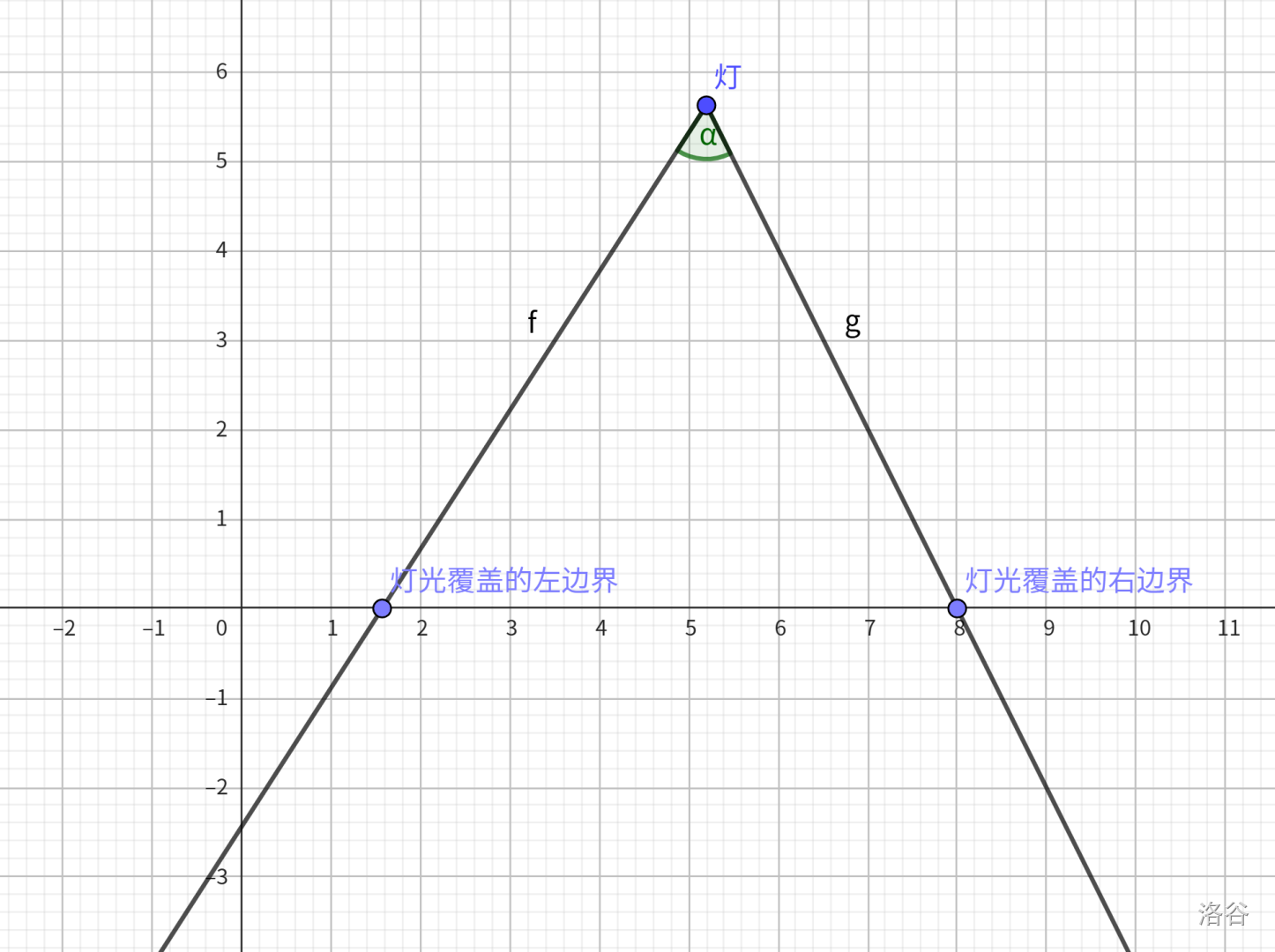
此时,已经知道了灯的位置 $(x_1,y_1)$,以及灯光覆盖的左边界 $(k_1,0)$,现在要求出灯光覆盖的右边界 $(k_2,0)$。
现在可以先求出 $(x_1,y_1)$ 指向 $(k_1,0)$ 的极角(极轴为 $x$ 轴正向),可以调用 C++ 函数 atan2(0-y,k-x1) 得到。
随后将这个角度加上 $\�lpha$ 就能得到 $(x_1,y_1)$ 指向 $(k_2,0)$ 的极角,令其为 $\theta$。
此时考虑构造一个以 $(x_1,y_1)$ 为中心的单位圆,算出其与穿过 $(x_1,y_1)$ 和 $(k_2,0)$ 的直线的交点的横纵坐标相对于 $(x_1,y_1)$ 为 $(sin(\theta),cos(\theta))$ 。
那么可以得到穿过 $(x_1,y_1)$ 和 $(k_2,0)$ 的直线的斜率是 $\frac{\sin(\theta)}{\cos(\theta)} = \tan(\theta)$。
那么现在可以得到:
$$
\tan(\theta)\cdot (k_2-x_1) = -y_1\
-\tan(\theta)x_1=-y_1 - \tan(\theta)\cdot k_2\
x_1 = \frac{y_1}{\tan(\theta)} + k_2\\
k_2 = x_1-\frac{y_1}{\tan(\theta)}
$$
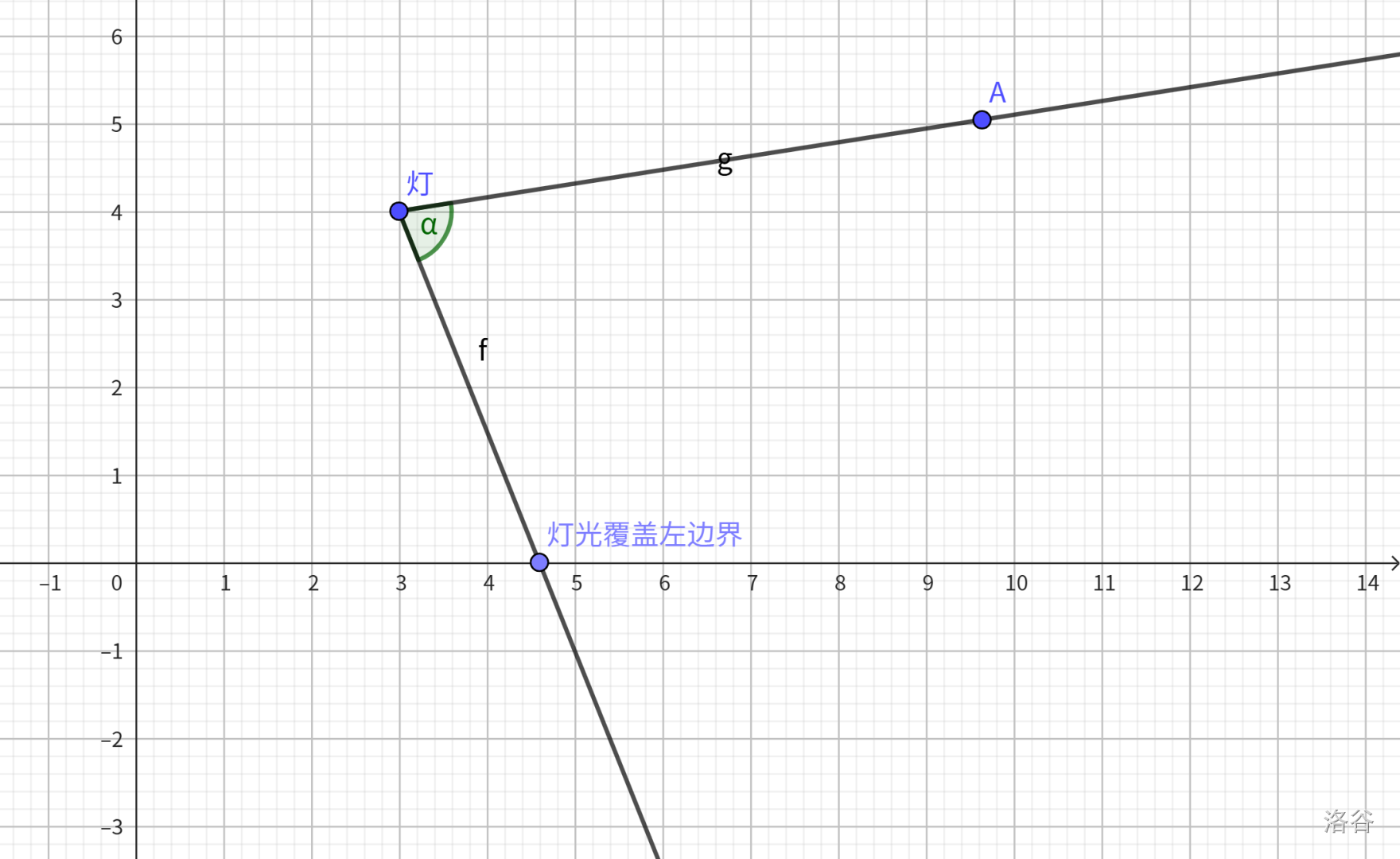
上述式子成功求出了灯光覆盖的右边界,需要注意若 $\theta \ge 0$,那么右边会延伸到无穷远,因为此时灯光覆盖区域大概长这个样子:
#include <bits\/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define FOR(i,a,b) for(auto i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
#define REP(i,a,b) for(auto i=(a);i>=(b);i--)
#define FORK(i,a,b,k) for(auto i=(a);i<=(b);i+=(k))
#define REPK(i,a,b,k) for(auto i=(a);i>=(b);i-=(k))
#define pb push_back
#define mkpr make_pair
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef pair<ll,ll> pll;
typedef vector<int> vi;
template<class T>
void ckmx(T& a,T b){
a=max(a,b);
}
template<class T>
void ckmn(T& a,T b){
a=min(a,b);
}
template<class T>
T gcd(T a,T b){
return !b?a:gcd(b,a%b);
}
template<class T>
T lcm(T a,T b){
return a\/gcd(a,b)*b;
}
#define gc getchar()
#define eb emplace_back
#define pc putchar
#define ep empty()
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pln pc('\n');
#define islower(ch) (ch>='a'&&ch<='z')
#define isupper(ch) (ch>='A'&&ch<='Z')
#define isalpha(ch) (islower(ch)||isupper(ch))
template<class T>
void wrint(T x){
if(x<0){
x=-x;
pc('-');
}
if(x>=10){
wrint(x\/10);
}
pc(x%10^48);
}
template<class T>
void wrintln(T x){
wrint(x);
pln
}
template<class T>
void read(T& x){
x=0;
int f=1;
char ch=gc;
while(!isdigit(ch)){
if(ch=='-')f=-1;
ch=gc;
}
while(isdigit(ch)){
x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(ch^48);
ch=gc;
}
x*=f;
}
void ioopti(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
}
typedef long double ld;
const ld pi=acos(ld(-1));
ld turn(ld jiaodu){
return jiaodu*(pi\/ld(180));
}
ld calc(pair<ld,ld> nd,ld deg,ld fir){
ld xcha=nd.fi-fir;
ld ycha=nd.se;
ld len=hypot(xcha,ycha);
xcha\/=len,ycha\/=len;
ld curdeg=atan2(-ycha,-xcha);
curdeg+=turn(deg);
ld dx=cos(curdeg),dy=sin(curdeg);
\/\/ printf("dx %.10Lf dy %.10Lf\n",dx,dy);
if(abs(dy)<1e-10){
if(dx>0)return 1e300;
return fir;
}
if(dy>0){
return 1e300;
}
return max(nd.fi+dx*(nd.se\/(-dy)),fir);
}
const int maxn=25;
int n;
ld l,r;
pair<ld,ld> nd[maxn];
ld a[maxn];
ld f[1<<21];
void solve(int id_of_test){
scanf("%d%Lf%Lf",&n,&l,&r);
FOR(i,1,n){
scanf("%Lf%Lf%Lf",&nd[i].fi,&nd[i].se,&a[i]);
}
int all=(1<<n)-1;
FOR(msk,0,all){
f[msk]=-1e18;
}
\/\/ printf("calc = %.10Lf\n",calc(nd[1],a[1],0.00001));
f[0]=l;
FOR(msk,0,all){
if(f[msk]<-1e10)continue;
FOR(i,1,n){
if(!(msk&(1<<(i-1)))){
ckmx(f[msk|(1<<(i-1))],calc(nd[i],a[i],f[msk]));
}
}
\/\/ printf("f[%d] = %.10Lf\n",msk,f[msk]);
}
printf("%.9Lf\n",min(f[all],r)-l);
}
int main()
{
int T;
T=1;
FOR(_,1,T){
solve(_);
}
return 0;
}
\/*
1. 对题意的理解能否和样例对的上?
2. 每一步操作,能否和自己的想法对应上?
3. 每一步操作的正确性是否有保证?
4. 是否考虑到了所有的 case?特别是极限数据。
5. 变量的数据类型是否与其值域匹配?
6. 时间复杂度有保证吗?
7. 空间多少 MB?
*\/



 鲁ICP备2025150228号
鲁ICP备2025150228号